GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Benthic: describes the habitat on, near, or in the bottom of a body of water. Benthic organisms may live within the sediment at the bottom of the ocean.
Biota: the living things that belong to an area or region.
Crowdsourcing: collecting information, data, opinions, and products from a group of people. Crowdsourcing often involves using web-based tools.
Degraded: in poor condition.
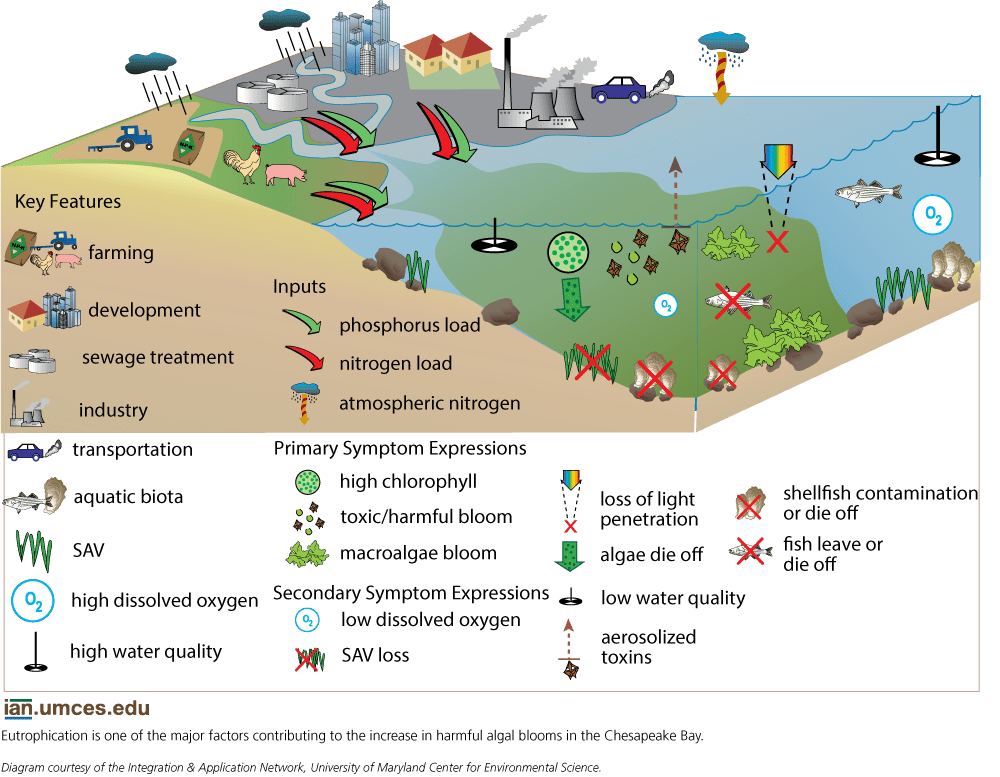
Eutrophication: buildup of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus in a body of water. Plants, algae, and bacteria may grow too much and become harmful, not leaving enough oxygen for other organisms. It “occurs when the environment becomes enriched with nutrients, increasing the amount of plant and algae growth to estuaries and coastal waters” (NOAA National Ocean Service). The conceptual diagram below illustrates the causes and effects of eutrophication in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. diagram by Jane Hawkey, Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library)
Food security is the ability to reliably and affordably access nutritious food. Food insecurity can happen when household income is low or inconsistent, or when grocery stores are absent, ill-supplied, or overly expensive. “Based on the 1996 World Food Summit, food security is defined when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.” (World Bank Group)
Groundwater is the water under the Earth’s surface. Groundwater is often used for drinking water and irrigation for agriculture.
Land-sea interface describes “the area that links terrestrial and marine habitats”, also called the “Coastal Transition Zone (CTZ)”. (Talley et al 2003)
Living shorelines is “a broad term that encompasses a range of shoreline stabilization techniques along estuaries, bays, tributaries, and other sheltered shorelines” (NOAA Habitat Blueprint). A shoreline designed to combat erosion using natural materials and techniques.
The diagram below provides an example of the benefits of living shorelines (bottom right) over hardened shorelines (top right) alongside other adaptations that can help protect properties from climate change events such as flooding. A hardened shorelines is a shoreline composed of rigid man-made structures such as seawalls or bulkheads.

Diagram by Jane Hawkey, Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library)
Nautilus describes “a cephalopod (a type of mollusk)—a distant cousin to squids, octopi, and cuttlefish”. Nautiluses live inside hard, chambered shells, (NOAA National Ocean Service). A photograph of a nautilus (left) and a nautilus symbol (right) are shown below.


Photograph by Dr. Katie May Laumann. Symbol by Tracey Saxby, Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library).
Nutrient flux is the movement of nutrients throughout an ecosystem. For example, erosion can cause nutrients from land to flow into bodies of water.
Physiological describes things related to the makeup and processes that allow the body of a living organism to function.
Physiology is the makeup and processes that allow the body of a living organism to function.
Rain garden is “a depressed area in the landscape that collects rain water from a roof, driveway or street and allows it to soak into the ground.” (EPA)
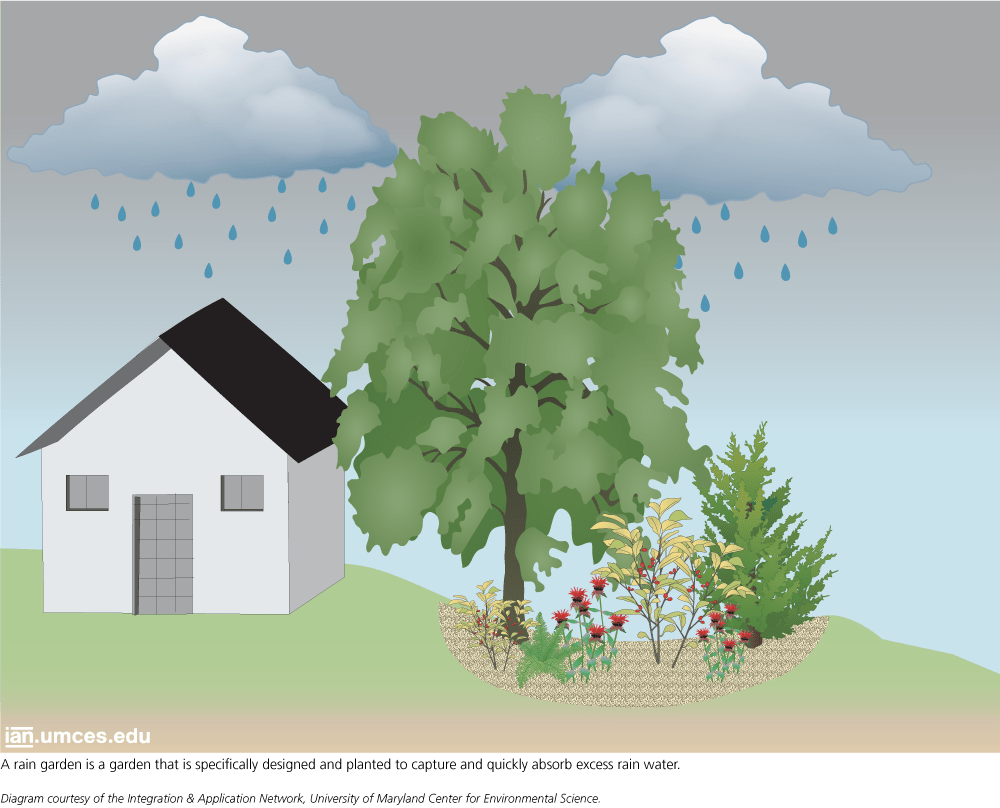
Diagram by Alexandra Fries, Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library)
Riparian describes the land area along a body of water, such as a wetland or wooded area along a river.
Salinity is the amount of salt in a body of water.
Sediment loading is the flow of sediment into a body of water.
Synthesis describes the bringing together of information, ideas, data, and expert opinion from multiple sources.
Glossary References:
1. EPA: United States Environmental Protection Agency, United States Government. “Rain Gardens.” Soak Up the Rain. https://www.epa.gov/soakuptherain/soak-rain-rain-gardens
2. NOAA Habitat Blueprint, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “What is a Living Shoreline?”. Living Shorelines. https://www.habitatblueprint.noaa.gov/living-shorelines/
3. NOAA National Ocean Service1, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “What is a nautilus?” Ocean Facts. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/nautilus.html
4. NOAA National Ocean Service2, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “What is eutrophication?” Facts. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/eutrophication.html
5. Talley, Drew M., North, Elizabeth W., Juhl, Andrew R., Timothy, David A., Conde, Daniel, deBrouwer, Jody F.C., Brown, Cheryl A., Campbell, Linda M., Garstecki, Tobias, Hall, Catherine J., Meysman, Filip J.R., Nemerson, David M., Souza Filho, Pedro W., Wood, Robert J. 2003. Research challenges at the land-sea interface. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science / 58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.010
6. World Bank Group. “What is Food Security?” Understanding Poverty. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/agriculture/brief/food-security-update/what-is-food-security